Photovoltaic power stations need to conduct daily safety inspections and periodic panel failure inspections to ensure the power generation efficiency of photovoltaic panels. However, photovoltaic power stations cover a wide area and have many potential safety hazards, making it difficult to achieve satisfactory results by manual inspection.
Unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with thermal imaging core can conduct rapid patrols, which can better meet the daily maintenance needs of photovoltaic power stations. Due to the high local temperature of photovoltaic modules with hot spots, by analyzing high-contrast thermal imaging images, the fault location can be seen and located at a glance, with results far exceeding our expectations.
What are the advantages of using thermal imaging technology for inspection?
-Intuitive: visual representation of heat distribution, clear and visible heat spots and temperature anomalies
-Efficient: check large areas in a short time, saving time and efficiency, and reducing maintenance costs
-Accurate: with accurate temperature measurement function that quickly locates the hot spots
-Safety: early detection of hot spots to prevent safety accidents
-All weather: 24-hour real-time imaging under harsh conditions such as total darkness, heavy fog, dust, wind, rain, snow etc.
-No interference: no power cut, non-contact detection, no interference with the original temperature field of the photovoltaic module
In fact, thermal imaging camera is one of the best operation and maintenance tools for preventive maintenance, condition monitoring, and fault diagnosis in the photovoltaic industry. In photovoltaic power stations, it can also be used for detecting hidden cracks, short circuits, open circuits, and other thermal defects in solar cell modules, as well as for fault detection of electrical equipment such as solar inverters, controllers, power distribution cabinets, and AC/DC lines.
So what problems can infrared thermal imaging technology detect?
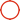
Photovoltaic panel hot spot detection
The hot spot effect is known as one of the four major fire hazards of photovoltaic modules. Efficient detection and timely disposal are crucial to the lifetime, power generation efficiency, safe and stable operation of the entire system.
Under solar irradiation, the temperature distribution of each battery module in normal operation is relatively uniform, and the hot spot effect refers to the temperature rise of some battery modules that is far greater than the surrounding battery modules, which can seriously damage the entire system.
Generally, hot spots are mainly caused by both external and internal causes. The majority of heat spots are caused by external factors. So, in daily operation and maintenance, it is necessary to remove the shielding timely to prevent potential problems.
The main external cause is that the surface of the module is blocked by bird droppings, dirt, fallen leaves, vegetation, etc., resulting improper working of the module, consuming the power of other batteries, and releasing heat to form heat spots.
Internal reasons are related to factors such as the production process and product quality of solar cell modules.
The most prominent manifestation of hot spots is temperature anomalies, and accurate temperature detection is the specialty of infrared thermal imagers.
Through accurate temperature measurement, infrared thermal cameras can sensitively sense the temperature changes on the surface of photovoltaic modules, easily obtain thermal information for each photovoltaic module, and visually present it on the screen. Abnormal high temperature battery modules can be identified at a glance. Then, the heat spot can be located immediately, so that assist staff can easily handle, repair, or replace battery components.
In addition to identifying and locating hot spots, it is also possible to perform preventive maintenance and condition monitoring on battery components, and deal with external factors as early as possible to prevent accidents.
The hot spot effect can lead to permanent damage such as burning of the battery, formation of dark spots, solder melting, etc. If not handled quickly, it can affect the life of the photovoltaic panel and affect power generation efficiency. The temperature of the photovoltaic module during normal operation is 30 ℃. When the local temperature is 6.5 ℃ higher than the surrounding temperature, hot spots may appear in the local parts of the module. Through visual imaging with a thermal camera, patrol inspectors can accurately determine the location of hot spots on the photovoltaic panel.